Basic Principles and Terms of Printing Color Management
Release Time: 2022-12-02 17:15:33.946
Color management has been paid attention to by more and more printing plants, and the basic principles and professional terms of color management have become our necessary knowledge. Only by mastering these knowledge, can we use instruments and systems to control our production process and achieve our quality goals with ease in daily production.
1、 Basic color principle
[Visible light] 380nm to 720nm is the range of light waves that can be sensed by the human eye, called "visible light", and beyond this range is called "invisible light"
[Invisible light] Below 380nm, there are ultraviolet light, X-ray, gamma ray, cosmic ray, etc; Above 720nm are infrared ray, microwave ray, radar ray, radio ray, etc
[Solar light] Solar light includes visible light and invisible light. For the reaction of the human eye, the light wave range from 400nm to 500nm is blue light, 500nm to 600nm is green light, and 600nm to 700nm is red light
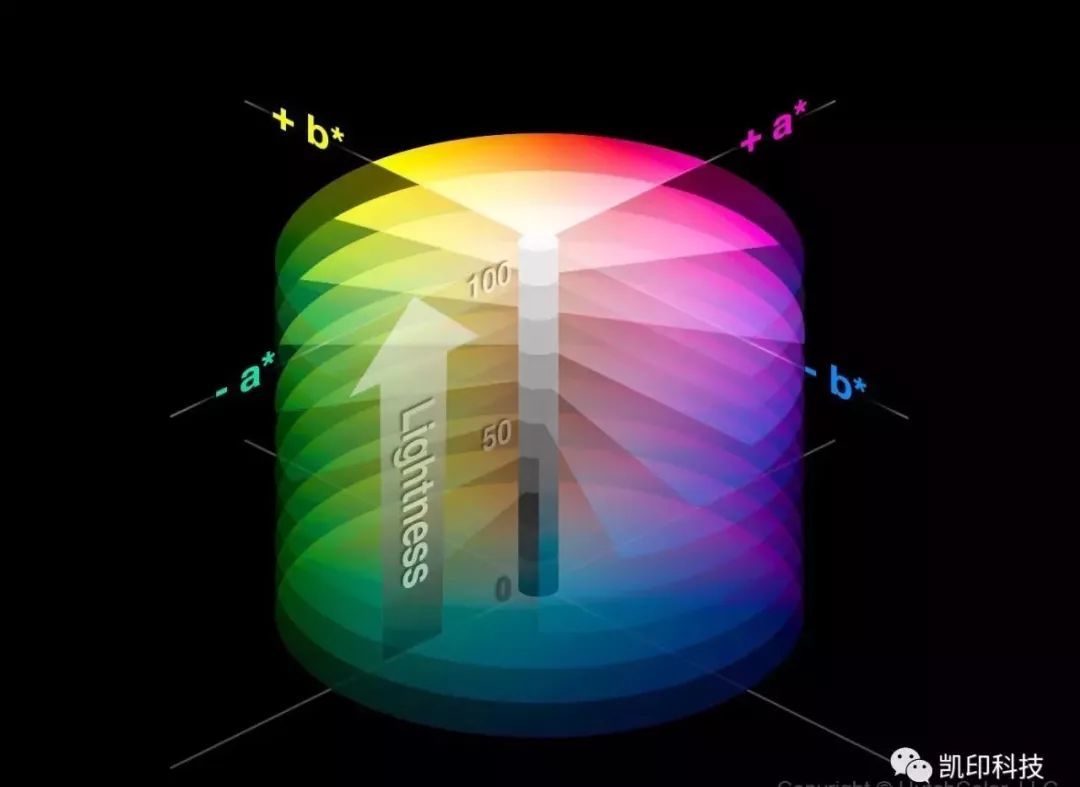
[Color adding system] Red (R), green (G) and blue (B) light are called the three primary colors in the color adding system, and they can be mixed to produce any color. Red light (R)+green light (G)=yellow light (Y), green light (G)+blue light (B)=cyan light (C), blue light (B)+red light (R)=magenta light (M). When combined with an equal amount of tricolor light, white light will appear. Blue (C), magenta (M) and yellow (Y) lights are the relative colors of red (R), green (G) and blue (B) lights respectively. Any pair of relative colored lights will also produce white light when mixed.
[Subtraction system] There are also three primary colors in the pigment (including printing ink), which are cyan (C), magenta (M) and yellow (Y). They belong to the subtractive system and represent the opposite of the three primary colors in the additive system. The addition of two colored lights will produce brighter colors, while the mixing of two pigments will produce darker colors, because the pigments absorb part of the visible light. Theoretically, the mixing of the three primary colors CMY in the pigment can produce any color, including black; In fact, their mixing will only produce part of the color, and the mixing of the same amount of CMY will only produce dark brown, not black. The reason is that today's pigments are not completely ideal, so black and spot colors are needed in printing ink to fill this shortcoming.
Cyan
Magenta
Yellow
BlacK
Red
Green
Blue
II Relationship between various color modes
RGB mode
It is composed of red, green and blue light, which is mainly used for the display of the display screen. Therefore, it is also called the color light mode. The light of each color is divided into 256 orders from 0 to 255. 0 indicates that the light does not exist, and 255 indicates that the light is most saturated, thus forming the RGB color light mode. Black is due to three kinds of light are not bright. The three kinds of light add together in pairs to form blue, magenta and yellow. The stronger the light is, the brighter the color is. Finally, the RGB three lights together are white, so the RGB mode is called additive color method.
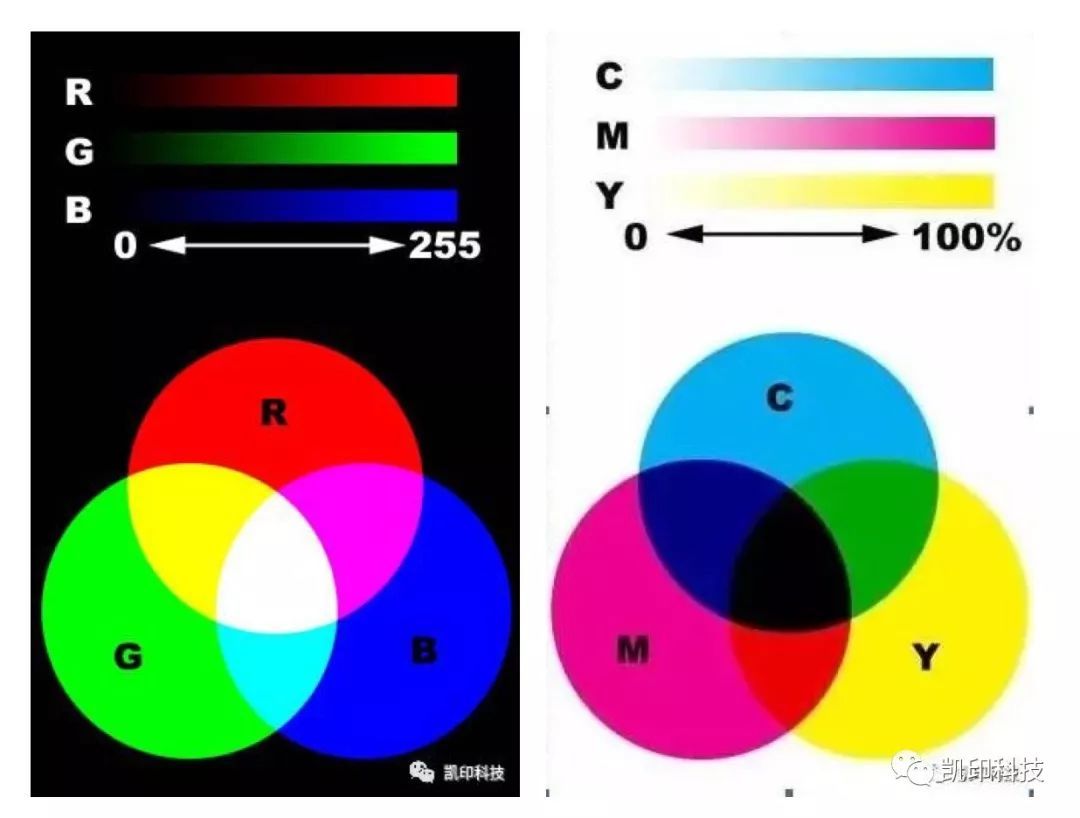
CMYK mode
It is composed of green, magenta, yellow and black inks. It is mainly used for printing, so it is also called the color pattern.
The usage of each kind of ink ranges from 0% to 100%. The three CMY inks are mixed to produce more colors, and the red, green, and blue colors are formed by adding the two together. Since the three CMY inks cannot form pure black in printing, a separate black ink K is required, thus forming the pigment mode of CMYK. The greater the amount of ink, the heavier and darker the color; On the contrary, the less ink, the brighter the color. When there is no ink, you will see white paper with nothing printed on it, so CMYK mode is called subtractive method.
Lab mode
It is a theoretical mode of recording light color.
CIE (Commission Internationale de l'Eclairage) is the abbreviation of the International Illumination Association. It formulates the international standard for measuring color and determines the color value.
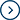
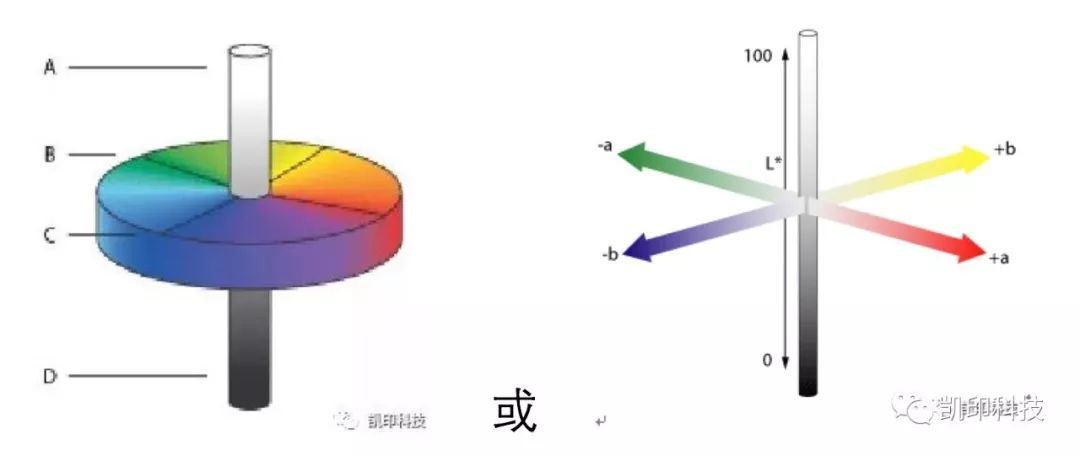
CIE has formulated L *, a * and b * values to measure the color value, which is called CIELAB
L * represents lightness, which varies from bright (at this time, L *=100) to dark (at this time, L *=0).
A * value indicates that the color changes from green (- a *) to red (+a *), while
The b * value indicates that the color changes from yellow (+b *) to blue (- b *).
After using the system, any color can find a corresponding position on its chart.
△ E: The distance between CIE L * a * b * color spaces of two colors is used to represent total color difference and establish quantitative color tolerance. Generally, △ E is calculated in a visually uniform chromaticity space.
The values of L, a, b and △ E on the printed matter can be measured with the spectrodensitometer eXact.
III Color gamut relationship of three modes
Each color has its corresponding color range, which is called color gamut.
Among RGB, CMYK and Lab color modes, Lab has the largest color gamut, which includes all visible light of human eyes. The colors people see are recorded according to the wavelength. What people can see is red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue and purple. The two ends of these rays also include infrared and ultraviolet rays. The wavelengths of these two optical fibers are too long or too short to be seen by the human eye, so they are excluded from the Lab. In other words, as long as we can see the light, the Lab includes. Lab color space is the intermediary of color conversion between various device related color spaces, and is the color space of independent devices. The color represented by a Lab value is unique. Therefore, the Lab color space is the connected color space for color management and the core of ICC profile.
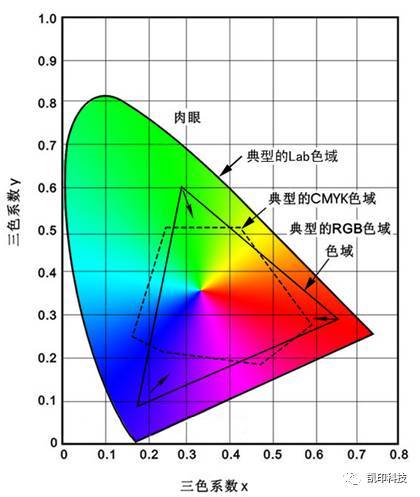
In the Lab, RGB colors are included, that is, the color gamut of RGB is smaller than that of the Lab. This also tells us that not all colors can be displayed on the display, such as gold, some fluorescent colors, etc.
Another area in the Lab is CMKY. In general, the color gamut of CMKY is smaller than that of RGB. A considerable part of the color gamut of the two colors overlap, but some colors in CMYK are outside of RGB. This also tells us that some printed colors cannot be correctly reflected on the display.
In actual work, you may have selected a very satisfactory color on the screen, and the color must be within RGB, just outside CMYK. When you need to print this image, you should be reminded that all printers are CMYK, and the printer will automatically convert the RGB color value to the closest CMYK value. This conversion has resulted in the obvious color difference between the printing color and the display color, excluding the error of all external factors such as printers, displays, and so on. This color difference is still inevitable. Therefore, when making images, we should correctly select the corresponding color mode according to the output requirements.
It can be clearly seen from the following figure that the obvious difference in color occurs after RGB mode is converted to CMYK mode.

The upper part of the image is the standard RGB tricolor, and the lower part is the change after conversion to CMYK. You can do this experiment yourself: use Photoshop to fill the RGB image with three color blocks: R255, G255, B255, and then press Ctrl+Y to switch between RGB and CMYK modes repeatedly and observe their differences.
IV Application of Color Difference Delta-E( Δ E)
1.CIE LAB
LAB color space is based on the theory that a color cannot be both blue and yellow. Therefore, a single value can be used to describe the red/green and yellow/blue badges. When CIE L * a * b * is used for a color, L * represents the value of lightness; A * represents red/green and b * represents yellow/blue values.
Note: CIE LAB △ E total color difference △ L+represents white, △ L - represents black, △ a+represents red, △ a - represents green, △ b+represents yellow, and △ b - represents blue
CIE LCH
CIE LCH color model uses the same color space as L * a * b *, but it uses L to represent the value of lightness; C is the saturation value and H is the cylindrical coordinate of the hue angle value.
2. Use Delta-E( Δ E) Method of determining color accuracy by measurement
After we know what color accuracy is and people's requirements for color accuracy, we should know how to determine color accuracy? Generally speaking, in the plate making and printing industry, people prefer to use Delta-E to measure, which is a measurement method to describe "difference", and can relatively easily measure and calculate the color accuracy.
3. What is Delta-E( Δ E) Measurement?
Most color measurements are done with instruments that measure CIELabs (the method of plotting color information collected by spectrometers). The comparison between colors is completed by mathematical comparison of the CIELab responses of the two groups and mathematical calculation of the differences between them. The value used to describe the difference is called Delta-E. Although Delta-E can be derived by arithmetic, it is usually described as the smallest difference in color and hue that can be detected by the human eye. When describing the differences in printed samples, the Delta-E value has been proved to be very effective due to the connection between Delta-E and people's perception. In the printing industry, Delta-E changes between 3 and 6 are generally considered acceptable.
Although the use of Delta-E measurement will be affected by the observer, ink and medium variability, a certain tolerance is allowed here, and some variability in ink and paper quality is tolerable. But there must always be a certain standard. What is the Delta-E variability of the standard? During the operation of the printing machine, the sampling interval for good commercial printing should not vary from more than 3 to 6 Delta-E units for the length of its operation.
Delta-E can quantify the accuracy of color restoration as a numerical value, which can accurately reflect the accuracy of color. Therefore, the smaller the value, the better. The higher the value, the more distorted the color.
4. Color effects in different Delta-E ranges:
【 Δ The E value is 1.6-3.2] The human eye can hardly distinguish the color difference, which is usually considered as the same color. There are only a few professional monitors, such as Yizhuo EIZO;
【 Δ The E value is 3.2-6.5] Professionally trained people can distinguish the difference, but ordinary people can't observe the difference, and the impression is basically the same.
【 Δ E value is 6.5-13] color difference can be seen, but it can be considered as the same tone;
【 Δ E values between 13-25] are considered as different tones, and those beyond this value are considered as different colors.
Based on this, the old printing press may experience greater changes than three to six Delta-E unit values, but whether this variability is accepted by the printer and the customer or not, it should be established before the printing press starts to work. When a piece of printing work exceeds the company's variability standard, the wisest thing to do is to stop printing and try to determine the cause of the variability. The printing work can continue only after the cause is determined and corrected.
5. Delta-E ( Δ E) Color difference formula:
-CIELab (1976) is widely used in offset printing
-CIE2000 optimal color difference formula, based on the improved version of CIELab (1976), is defined as a new standard by ISO
-CMC is widely used in printing and dyeing industry
-CIE94 is applied in textile field
V Color measurement mode
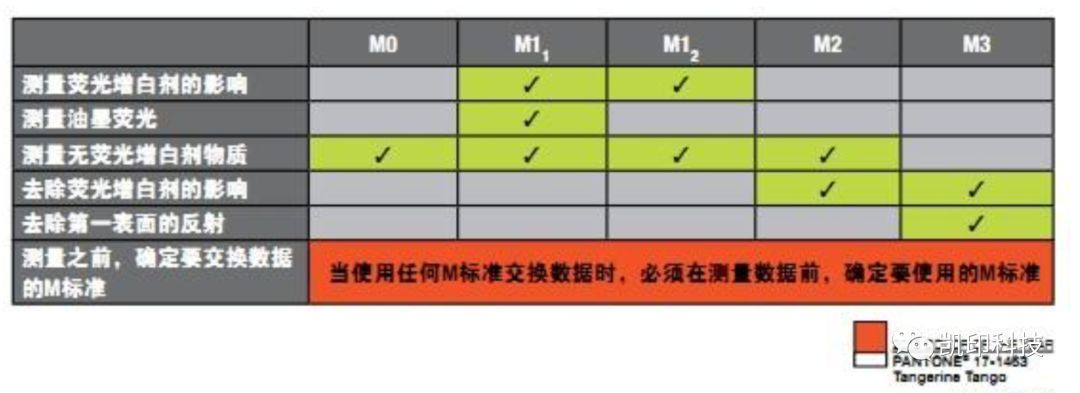
Application of M measurement modes M0, M1, M2 and M3
• Theoretically, the use occasions of each measuring lighting condition are relatively clear
• M0 is applicable to the case where both the substrate and imaging pigment do not contain fluorescent whitening agent.
• M1 is applicable to substrate or imaging pigment, or both contain fluorescent whitening agent. It is also applicable to the case that the substrate contains fluorescence, and the fluorescence characteristics need to be collected, and it can be confirmed that the imaging pigment does not contain fluorescence.
• M2 is used for paper fluorescence, but it is also hoped to eliminate the impact of data.
• M3 is used for special purposes, i.e. the first surface reflection should be reduced, including the use of polarized light.
VI Density standard selection
ISO T status
T state is a wide band response, which is widely used in North America's printing process industry. It is also the most commonly used measurement state in our printing and packaging process.
ISO E status
E state is the European standard, using Wratten 47B filter. Compared with T state, it has a higher yellow count.
ISO A status
State A is usually used in photography, bookbinding and finishing industries.
ISO I Status
Specially designed for measuring tricolor printing ink on paper. The measurement of non tri color printing ink may cause slight inconsistency.
Xrite G status
The wide wave band response specially designed for the printing process is similar to the T-type, but it is sensitive to the thicker yellow ink.
The most commonly used measurement condition in China's printing is the ISO T status, which is also the default measurement status of many instruments. In practical applications, we should also pay attention to the quality inspection requirements, and determine the final measurement conditions according to the actual quality inspection requirements.
7、 Glossary of Color Management
1. Metamerism
When a pair of colors are in a certain light source, the colors are the same, but in another light source, the colors are different. This phenomenon is called "metamerism".
2. ColorTemperature
Measurement of the color light emitted by an object when it is heated. Color temperature is usually expressed by absolute temperature or Kelvin degree. Low color temperature such as red is 2400 ° K, high color temperature such as blue is 9300 ° K, and neutral color temperature such as gray is 6500 ° K.
3. Opacity
The hiding power index can reflect the covering ability of the coating ink to the substrate. If the covering power is higher, the paint or ink is not easy to change due to the color of the substrate.
4. Colorimeter
An optical measuring instrument that simulates the response of human eyes to red, green and blue light.
5. Reflectance curve
A graph showing the reflectivity of an object to light of different wavelengths.
6. D50
Represents a CIE standard illuminant with a color temperature of 5000 ° K. In the printing industry, this color temperature is widely used to make observation light boxes.
7. Reflectance
Describe the percentage of light reflected from the object surface. Use a spectrophotometer to measure the reflectivity of objects at different intervals along the visible spectrum. If the visible spectrum is abscissa and the reflectivity is ordinate, the spectral curve of object color can be drawn.
8. D65
Represents a CIE standard illuminant with a color temperature of 6504 ° K. It is a commonly used test illuminator.
9. Spectrophotometer
A measuring instrument used to measure the reflection or transmission characteristics of light waves through objects, and express the measurement results as spectral data.
10. Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic wave radiation band that propagates in the air with different sizes is expressed by wavelength. Different wavelengths have different properties, and many wavelengths are invisible to the human eye. Only the electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength between 380 and 720 nm is visible to the human eye. Beyond the visible light waves are invisible, such as T rays, X rays, microwaves and infinite radio waves.
11. SpecularExcluded (SCE, SPEX, Ex)
When an integrating sphere spectrophotometer is used to measure an object, the specular reflection of the object will not be measured. Therefore, when the specular reflection data is excluded from the measurement, the instrument will consider the influence of the surface texture of the object on the color.
12. Specular included (SCI, SPIN, In) (including specular reflection)
When using the integrating sphere instrument to measure an object, the specular reflection of the object will be measured at the same time. Therefore, when the measurement contains specular reflection data, the instrument will only measure the color data of the object's pigment, regardless of the surface texture.
13. Hue
The basic colors of objects, such as red, green, purple, etc., can be determined by the angular position of the cylindrical color space or the position on the color wheel.
14. Strength
The strength is to calculate the batch difference between pigments.
15. Lightness
The depth of the color.
16. Tolerance
Acceptable difference between standard and sample measurements. (See Delta error)
17. Illuminator
The spectral distribution is used to describe the energy distribution of the light source.
18. Whiteness
Whiteness is the degree to which the color tends to be white, which is widely used in printing and textile industry.
19. llluminantA (light source A)
The CIE standard light source represented by the incandescent lamp, yellow orange, has a color temperature of 2856 ° K.
20. Yellowness
Yellowness refers to the deviation between color and standard white, which is widely used in the plastic industry.
21. llluminant C (C light source)
The tungsten filament lamp simulating the average sunlight is the representative standard light source, such as blue, and the related color temperature is 6774 ° K.
22. llluminantD (D light source)
The CIE standard light source represented by fluorescent lamp is based on the real measured spectrum of sunlight, and the related color temperature is 6504 ° K. D50, D65, and D75 are the most commonly used color temperatures.
Some of the pictures and texts in this site are collected and collated from the network for learning and exchange only. The copyright belongs to the original author. If you have violated your rights, please contact us to delete them in time.
More News
Shenzhen is a city of innovation and entrepreneurship. There are many small and medium-sized enterprises with high growth, often with huge potential and irreplaceable position in their respective fields. Shenzhen Satellite TV Finance Channel is the only authoritative local financial media in Shenzhen. Through Shenzhen Enterprise Power, it aims to tell the story of Shenzhen enterprises and show Shenzhen's innovative vitality.
Kaiyin Technology | Strength won the national high-tech enterprise recognition
At the beginning of the spring of 2020, Kaiyin Technology has received good news. In accordance with the relevant provisions of the Measures for the Administration of the Recognition of High tech Enterprises and the Guidelines for the Administration of the Recognition of High tech Enterprises issued by the State Administration of Taxation, Shenzhen Kaiyin Science and Technology Co., Ltd. was successfully recognized as a national high-tech enterprise in December 2019 through layer upon layer review in the selection of national high-tech enterprises.
"Color Data Lab" of Aisele Kaiyin was established
On July 22, 2019, Shenzhen Kaiyin Technology Co., Ltd., located on the 40th floor of Changping Business Building, Futian District, Shenzhen Bay, was authorized by Mr. Elton Pan, the general manager of Aiselei Greater China, on behalf of Aiselei, to Mr. Chen Shaozhong, the technical director of Shenzhen Kaiyin Technology Co., Ltd. So far, the long-awaited "color data laboratory" of Aisele Kaiyin was officially established. It has also become the first "color data laboratory" co established by Aiseli in Shenzhen. This will certainly provide a good interactive color management training, communication and experimental platform for printing and packaging enterprises.
Application Practice of Ashley eXact Measuring Instrument - Best Match!
Every printing work order, we have to face a problem, how to keep up with the "goal". The printing buyer gives you a target data, chromaticity/density/color difference... or a target sample... or an international standard Gracol 2006/Gracol 2013, Fogra 39/Fogra 51


Service Hotline:
180 8888 0185
Address:
605, Building B1, Funian Plaza, No. 3, Shihua Road, Futian District, Shenzhen, Guangdong
Tel:
Fax:
Email:





Copyright ©Shenzhen Kaiyin Technology Co., Ltd 粤ICP备16126578号 SEO
Website support:300.cn ShenZhen
Mobile: 180 8888 0185
Tel: +86 755 8280 8180
Address: 305A, Floor 3, Building B1, Funian Plaza, No. 3, Shihua Road, Futian District, Shenzhen, Guangdong
Email: service@kngcolor.com
We will give you feedback in time